 |
CMSIS-Core (Cortex-M)
Version 5.1.1
CMSIS-Core support for Cortex-M processor-based devices
|
 |
CMSIS-Core (Cortex-M)
Version 5.1.1
CMSIS-Core support for Cortex-M processor-based devices
|
To use the CMSIS-Core (Cortex-M) the following files are added to the embedded application:
The Startup File startup_<device>.s is executed after reset and calls SystemInit. After the system initialization control is transferred to the C/C++ run-time library which performs initialization and calls the main function in the user code. In addition the Startup File startup_<device>.s contains all exception and interrupt vectors and implements a default function for every interrupt. It may also contain stack and heap configurations for the user application.
The System Configuration Files system_<device>.c and system_<device>.h performs the setup for the processor clock. The variable SystemCoreClock indicates the CPU clock speed. System and Clock Configuration describes the minimum feature set. In addition the file may contain functions for the memory BUS setup and clock re-configuration.
The Device Header File <device.h> is the central include file that the application programmer is using in the C source code. It provides the following features:
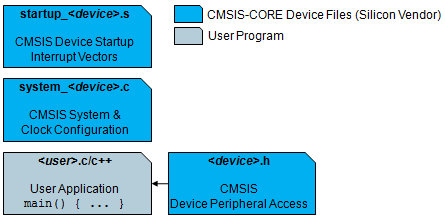
The CMSIS-Core (Cortex-M) are device specific. In addition, the Startup File startup_<device>.s is also compiler vendor specific. The various compiler vendor tool chains may provide folders that contain the CMSIS files for each supported device.
For example, the following files are provided in MDK to support the STM32F10x Connectivity Line device variants:
| File | Description |
|---|---|
| ".\ARM\Startup\ST\STM32F10x\startup_stm32f10x_cl.s" | Startup File startup_<device>.s for the STM32F10x Connectivity Line device variants. |
| ".\ARM\Startup\ST\STM32F10x\system_stmf10x.c" | System Configuration Files system_<device>.c and system_<device>.h for the STM32F10x device families. |
| ".\ARM\INC\ST\STM32F10x\stm32f10x.h" | Device Header File <device.h> for the STM32F10x device families. |
| ".\ARM\INC\ST\STM32F10x\system_stm32f10x.h" | system_Device.h Template File for the STM32F10x device families. |
Thereafter, the functions described under Reference can be used in the application.
Examples